
Testing and Treating LEMS
Understanding how your doctor will diagnose and treat your symptoms
Once you’ve found a neuromuscular specialist, the next steps on the road to feeling better are diagnosis and treatment. In this section, you’ll learn about some of the diagnostic tests that your doctor may use to identify the cause of your symptoms. If you are diagnosed with Lambert-Eaton myasthenic syndrome (LEMS), your doctor will prescribe a treatment based on the type of LEMS that you have.
Testing for LEMS
There are 3 common testing methods used to diagnose neuromuscular symptoms. After testing, your doctor will be able to tell you whether you have LEMS, MG, or another disorder.
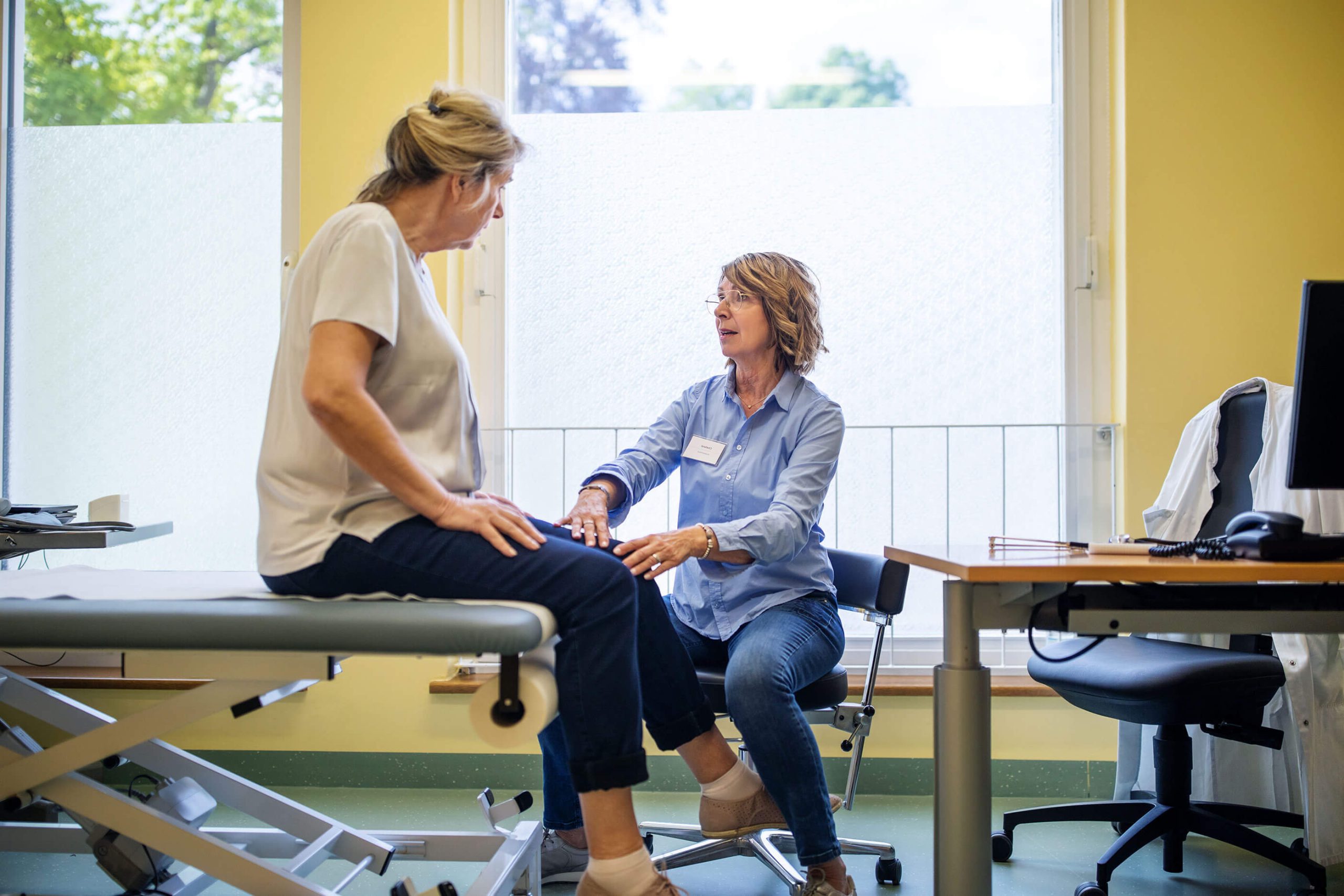
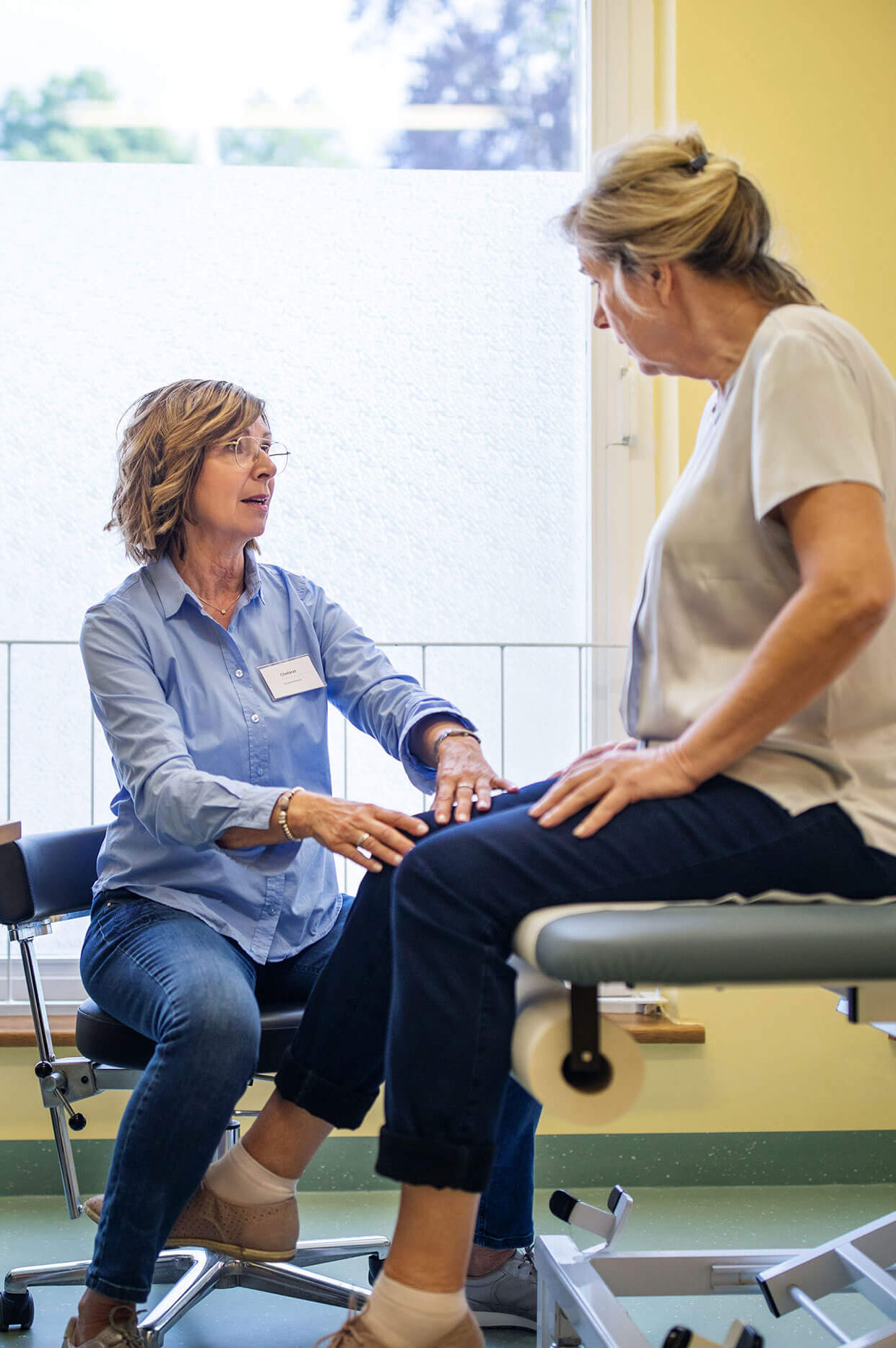
A physical exam
to evaluate your symptoms and test your reflexes. A diagnosis can be suspected based on this physical exam.
TO CONFIRM DIAGNOSIS, YOU DOCTOR MAY ORDER ADDITIONAL TESTS
A blood test
to check for the presence of certain antibodies special proteins made by your immune system
An electrodiagnostic test
to measure how well your muscles and nerves are communicating with each other.
What these tests will reveal
The results of LEMS testing will point your doctor to one of two different treatment paths:
A positive result will signal your doctor to start treatment for LEMS but also to screen you for cancer, which is present in more than half of all patients with LEMS.*
A negative result will tell your doctor to look for a cause other than LEMS for your symptoms.
*LEMS and cancer
In some cases, LEMS may be linked to an underlying cancer—usually in people with a history of tobacco smoking. In those cases, the doctor may do a special screening test first to rule out the presence of cancer. Read more about this type of LEMS on the next page.
Treating LEMS
There are several types of therapies that have been used to treat LEMS. Here are two options your doctor may consider:
Oral medicine
The recommended treatment for LEMS is an oral potassium channel blocker that is prescribed to help nerve signals reach the muscles
Infusion treatments
- Though not FDA-approved for LEMS, infusion therapiesmedicines that are administered through a needle or a catheter are sometimes prescribed to help provide additional symptom control
- Infusion treatments may be used along with symptomatic treatments such as a potassium channel blocker
- Clinical data suggest that infusion therapies may provide patients with a short-term benefit
Discover an FDA-approved treatment option for LEMS
Learn more about this therapy now
